PRESENT PERFECT
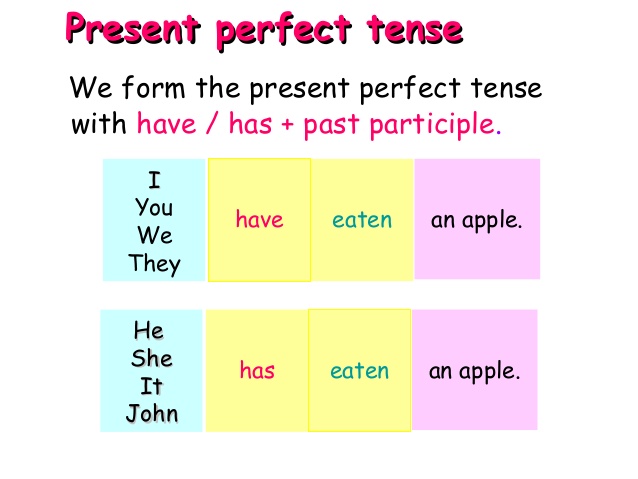
The present perfect tense refers to an action or state that either occurred at an indefinite time in the past (e.g., we have talked before) or began in the past and continued to the present time (e.g., he has grown impatient over the last hour). This tense is formed by have/has + the past participle.
He construction of this verb tense is straightforward. The first element is have or has, depending on the subject the verb is conjugated with. The second element is the past participle of the verb, which is usually formed by adding -ed or -d to the verb’s root (e.g., walked, cleaned, typed, perambulated, jumped, laughed, sautéed) although English does have quite a few verbs that have irregular past participles (e.g., done, said, gone, known, won, thought, felt, eaten).
EJEMPLOS
These examples show how the present perfect can describe something that occurred or was the state of things at an unspecified time in the past.
- I have walked on this path before.
- We have eaten the lasagna here.
The important thing to remember about the present perfect is that you can’t use it when you are being specific about when it happened.
I have put away all the laundry.
You can use the present perfect to talk about the duration of something that started in the past is still happening.
- She has had the chickenpox since Tuesday.
Use the verbs between paranthesis in the present
perfect. If there is an adverb, place it in the correct place. The sentences
can be affirmative, negative or interrogative.
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario